The theoretical maximum speed of a Wi-Fi network is indicated by its Wi-Fi standard 802.11. speed for wifi Like most computer networks, Wi-Fi supports different levels of performance, contingent on the technology standard. Now, the fastest normal is Wi-Fi 6, the shared name given to the IEEE 802.11ax wireless normal introduced in 2019. The 802.11ax normal is more common, but that will soon alteration as more Wi-Fi 6 devices enter the market speed for wifi.
Wi-Fi standards are certified by the Organization of Electrical and Electronics Engineers. Each Wi-Fi standard is rated by its theoretical maximum network bandwidth speed for wifi. However, the performance of Wi-Fi networks does not reach these theoretical maximums. The actual haste of a Wi-Fi wireless network connection depends on several factors.
Tips: Before purchasing a router, confirm that it is running the current version of 802.11 along with several previous iterations. Older routers, which sell at a low price because they are used, may be rated no higher than 802.11n or earlier.
Theoretical vs. Actual Network Speeds

Today’s Wi-Fi networks support a variety of standards.
An 802.11b network typically does not operate at more than 50 per cent of its theoretical maximum, around 5.5 Mbps 802.11a and 802.11g networks usually do not operate at more than 20 Mbps, Although 802.11n speeds reach a comparable 60 Mbps. Fast Ethernet at 100 Mbps, Ethernet connection can often outperform 802.11n in real-world use. However, Wi-Fi presentation continues to improve with each new generation of technology.
You will experience a wide variation in the actual and theoretical speeds of most of today’s Wi-Fi networks:
| Theoretical | Actual | |
| 802.11b | 11 Mbps | 5.5 Mbps |
| 802.11a | 54 Mbps | 20 Mbps |
| 802.11g | 54 Mbps | 20 Mbps |
| 802.11n | 600 Mbps | 100 Mbps |
| 802.11ac | 1,300 Mbps | 200 Mbps |
| 802.11ax | 10 Gbps | 2 Gbps |
What’s Next?
The following wireless communication standard will be 802.11be (Wi-Fi 7), which is likely to be finalized by IEEE in 2024. However, in practice, 802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6) is still gaining ground against 802.11ac (Wi-Fi For For 5).
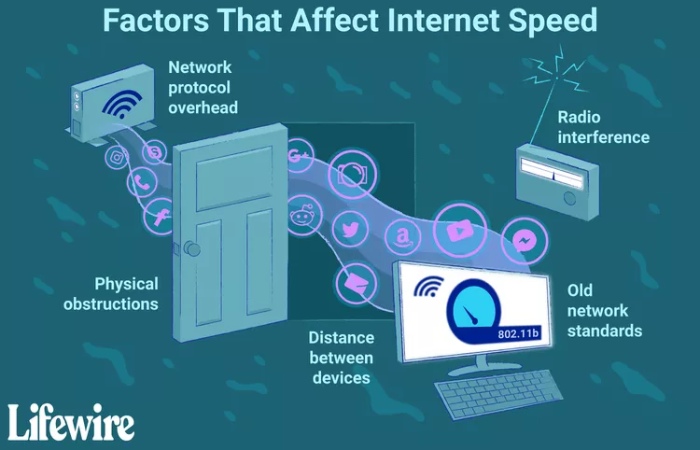
Factors Limiting Wi-Fi Connection Speeds

The difference between theoretical and practical Wi-Fi presentation comes from network procedure overhead, radio interference, physical obstacles in the line of sight between devices, and the distance between devices speed for wifi.
Additionally, as more devices communicate over the network concurrently, performance decreases due to how bandwidth works and the limits of the network hardware speed for wifi.
A Wi-Fi network joining operates at the highest possible speed that both devices, often called endpoints, support. An 802.11g laptop linked to an 802.11n router, for example, is connected at the lowest speed of an 802.11g laptop. Both devices must support the same normal to function at top speed.
The Role Internet Service Breadwinners Play in Network Speed (speed for wifi)
In-home networks, the presentation of an Internet connection is often the limiting factor in end-to-end net speed speed for wifi. Although most home networks allow file sharing within the home at speeds of 20 Mbps or higher, Wi-Fi clients still connect to the Internet at generally lower speeds supported by Internet service providers speed for wifi.
Most Internet service providers offer several levels of Internet service. The faster the joining, the more you pay speed for wifi.
The Increasing Importance of Network Speed (speed for wifi)
High-speed connections have become more critical as video streaming has gained popularity. You may have a payment to Netflix, Hulu, or another video streaming service. Still, if your Internet connection and network can’t meet the least speed requirements, you won’t be able to watch many movies.
The same can be said for video cyclosis apps. If you watch TV with a Roku, Apple TV speed for wifi, or other streaming entertainment accessory, you spend much of your TV time on commercial channel apps and premium services speed for wifi. Without a fast enough network, you can expect to knowledge poor video quality and frequent pauses to load the buffer speed for wifi.
For example, Netflix indorses a broadband connection speed of 1.5 Mbps but recommends higher speeds for advanced quality: 3.0 Mbps for SD quality, 5.0 Mbps for HD excellence, and 25 Mbps for Ultra HD quality.
How to Test Your Network Speed
Your Internet Service Provider may provide you with an online speed test service speed for wifi. Log in to your account, go to the joining speed page and ping the service. Repeat the test at different times of the day to obtain an average reference value.

